
- #Bound states energy levels finite quantum calculator trial#
- #Bound states energy levels finite quantum calculator free#
To evaluate the convergence, the process can be repeated. This calculation process works best when the potential is very large compared to the calculated energy. This gives a refined effective well width of L = x 10^ m = nm= fermi,Īnd a refined ground state energy estimate: The infinite well ground state (n=1) energy is E = x 10^ joule = eV= MeV, = GeV.įor potential U 0 = x 10^ joule = eV= MeV,Ī first estimate of the attenuation coefficient = x10^ m -1. Then the value of α can be refined by iteration to get an effective well width and a numerical solution for the energy.Īnd mass = x 10^ kg = m e = m p = MeV/c 2,
#Bound states energy levels finite quantum calculator trial#
One way to estimate the ground state energy of a finite potential well is to use the infinite well energy to produce a trial attenuation factor α. Since both sides of the equation are dependent on the energy E for which you are solving, the equation is trancendental and must be solved numerically. The ground state solution for a finite potential well is the lowest even parity state and can be expressed in the form where.
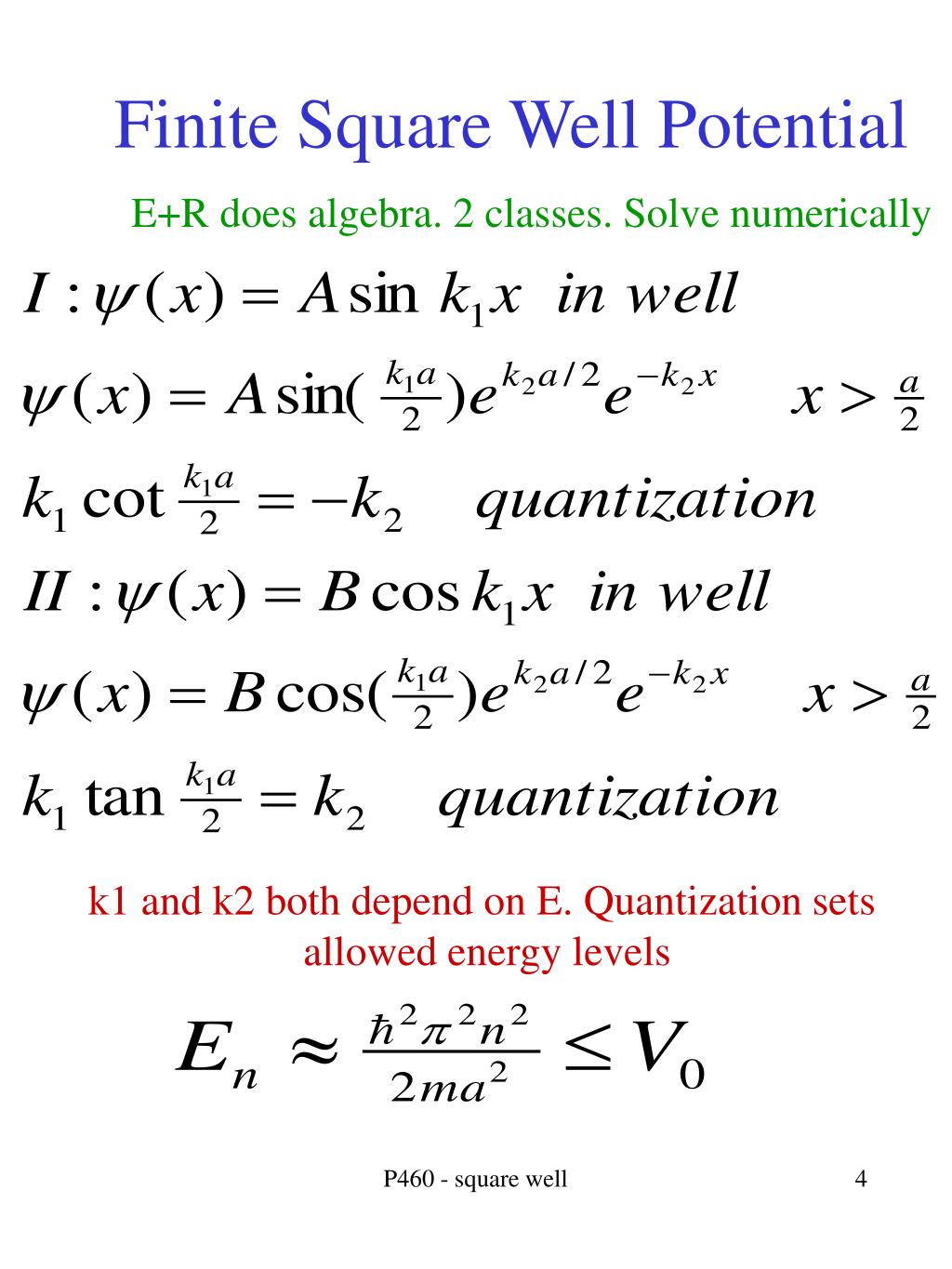
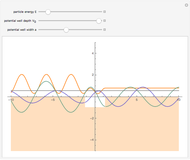
Applying such constraints is often the way that the solution is forced to fit the physical situation. The standard constraints on the wavefunction require that both the wavefunction and its derivative be continuous at any boundary. This last step makes use of the substitution that was used in the setup of the finite well problem: The Schrodinger equation gives trancendental forms for both, so that numerical solution methods must be used. Given a potential well as shown and a particle of energy less than the height of the well, the solutions may be of either odd or even parity with respect to the center of the well.

For the weak interaction, the Z boson's mass is 91.1876 ☐.0021 GeV/ c 2, which prevents the formation of bound states between most particles, as it is 97.2 times the proton's mass and 178,000 times the electron's mass. Because the photon is massless, D is infinite for electromagnetism. In relativistic quantum field theory, a stable bound state of n particles with masses. Examples include certain radionuclides and electrets.
#Bound states energy levels finite quantum calculator free#
In general, the energy spectrum of the set of bound states is discrete, unlike free particles, which have a continuous spectrum.Īlthough not bound states in the strict sense, metastable states with a net positive interaction energy, but long decay time, are often considered unstable bound states as well and are called "quasi-bound states". One consequence is that, given a potential vanishing at infinity, negative-energy states must be bound. The potential may be external or it may be the result of the presence of another particle in the latter case, one can equivalently define a bound state as a state representing two or more particles whose interaction energy exceeds the total energy of each separate particle. In quantum physics, a bound state is a quantum state of a particle subject to a potential such that the particle has a tendency to remain localized in one or more regions of space.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
